curl是常用的命令行工具,用来请求Web服务器。它的名字就是客户端的URL工具的意思。它的功能非常强大,命令行参数多达几十种。如果熟练的话,完全可以取代Postman这一类的图形界面工具。
- 本文转自 curl 的用法指南

OpenSource: 总结的快捷键使用文档
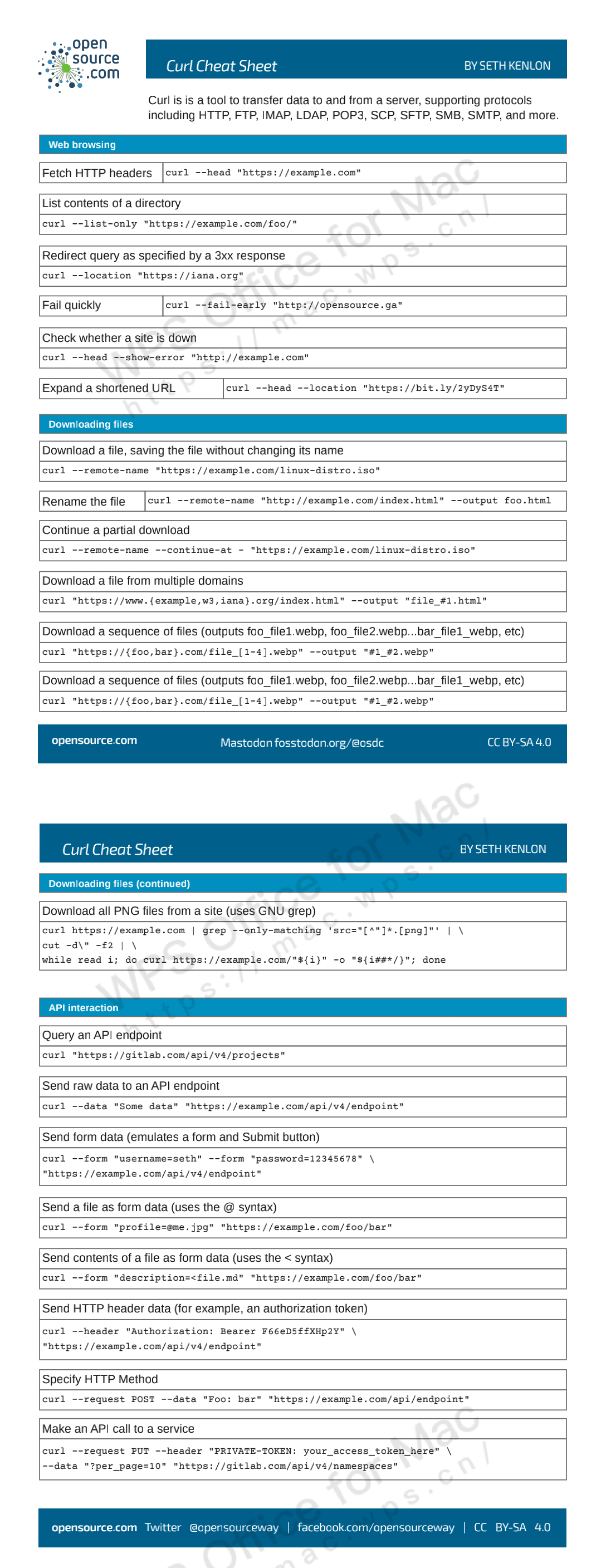
本文介绍它的主要命令行参数,作为日常的参考,方便查阅。不带有任何参数时,curl 就是发出 GET 请求。
# 向www.example.com发出 GET 请求
$ curl https://www.example.com
1. -A 用户代理
也可以通过
-H参数直接指定标头更改User-Agent配置
- 通过
-A参数指定客户端的用户代理标头(User-Agent),而在默认的情况下curl的默认用户代理字符串是curl/[version],其中version表示对应的版本号。
# 将User-Agent改成Chrome浏览器
$ curl -A 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/76.0.3809.100 Safari/537.36' https://google.com
# 移除User-Agent标头
$ curl -A '' https://google.com
# 通过-H参数直接指定标头更改User-Agent配置
$ curl -H 'User-Agent: php/1.0' https://google.com
2. -b 发送 Cookie 信息
- 通过
-b参数用来向服务器发送自定义的Cookie信息。
# Cookie: foo=bar
# 会生成一个标头向服务器发送一个名为foo,且值为bar的Cookie信息
$ curl -b 'foo=bar' https://google.com
# 发送两个Cookie信息
$ curl -b 'foo1=bar' -b 'foo2=baz' https://google.com
# 读取cookies.txt本地文件的Cookie信息,并将其发送到服务器
$ curl -b cookies.txt https://www.google.com
3. -c 将 Cookie 写入文件
- 通过
-c参数将服务器设置的Cookie写入一个文件
# 将服务器的HTTP回应所设置Cookie写入cookies.txt文本文件
$ curl -c cookies.txt https://www.google.com
4. -d 发送 POST 请求的数据体
--data-urlencode等同于-d 参数,发送 POST 请求的数据体,区别在于会自动将发送的数据进行 URL 编码
- 通过
-d参数用于发送POST请求的数据体。使用-d参数以后,HTTP请求会自动加上标头Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded。并且会自动将请求转为POST方法,因此可以省略-X POST参数。
# 发送POST请求的数据体
$ curl -d 'login=emma&password=123'-X POST https://google.com/login
$ curl -d 'login=emma' -d 'password=123' -X POST https://google.com/login
# 读取data.txt文件的内容,作为数据体向服务器发送
$ curl -d '@data.txt' https://google.com/login
# 发送的数据hello world之间有一个空格,需要进行URL编码
$ curl --data-urlencode 'comment=hello world' https://google.com/login
5. -e 设置 HTTP 的标头 Referer 字段
- 通过
-e参数用来设置HTTP的标头Referer,表示请求的来源。
# 将Referer标头设为https://google.com?q=example
$ curl -e 'https://google.com?q=example' https://www.example.com
# 通过-H参数可以通过直接添加标头Referer达到同样效果
$ curl -H 'Referer: https://google.com?q=example' https://www.example.com
6. -F 向服务器上传二进制文件
- 通过
-F参数用来向服务器上传二进制文件。
# 下面命令会给HTTP请求加上标头Content-Type: multipart/form-data
# 然后将文件photo.png作为file字段上传,类似于postman中的上传文件一样
$ curl -F '[email protected]' https://google.com/profile
- 通过
-F参数可以指定MIME类型。
# 指定MIME类型为image/png
# 否则curl会把MIME类型设为application/octet-stream
$ curl -F '[email protected];type=image/png' https://google.com/profile
- 通过
-F参数也可以指定文件名。
# 原始文件名为photo.png,但是服务器接收到的文件名为me.png
$ curl -F '[email protected];filename=me.png' https://google.com/profile
7. -G 构造 URL 的查询字符串
- 通过
-G参数用来构造URL的查询字符串。
# 下面命令会发出一个GET请求,如果省略-G参数会发出一个POST请求
# 实际请求的URL地址为 => https://google.com/search?q=kitties&count=20
$ curl -G -d 'q=kitties' -d 'count=20' https://google.com/search
# 如果数据需要URL编码,可以结合--data--urlencode参数
$ curl -G --data-urlencode 'comment=hello world' https://www.example.com
8. -H 添加 HTTP 请求的标头
- 通过
-H参数添加HTTP请求的标头。
# 添加HTTP标头 Accept-Language: en-US
$ curl -H 'Accept-Language: en-US' https://google.com
# 添加两个HTTP标头
$ curl -H 'Accept-Language: en-US' -H 'Secret-Message: xyzzy' https://google.com
# 添加 HTTP 请求的标头是Content-Type: application/json
# 然后通过-d参数发送JSON数据发送到服务器上面
$ curl -d '{"login": "emma", "pass": "123"}' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' https://google.com/login
9. -i 打印服务器回应的 HTTP 标头
- 通过
-i参数打印出服务器回应的HTTP标头。
# 下面命令收到服务器回应后,先输出服务器回应的标头,然后空一行,再输出网页的源码
$ curl -i https://www.example.com
10. -I 打印服务器回应的 HEAD 标头
- 通过
-I参数向服务器发出HEAD请求,然会将服务器返回的HTTP标头打印出来。
# 输出服务器对HEAD请求的回应
$ curl -I https://www.example.com
# --head参数等同于-I参数
$ curl --head https://www.example.com
11. -k 跳过 SSL 检测
- 通过
-k参数指定跳过SSL检测。
# 不会检查服务器的SSL证书是否正确
$ curl -k https://www.example.com
12. -L 跟随服务器的重定向
- 通过
-L参数会让HTTP请求跟随服务器的重定向,而curl默认不跟随重定向。
# 请求跟随服务器的重定向
$ curl -L -d 'tweet=hi' https://api.twitter.com/tweet
13. –limit-rate 限制请求和回应的带宽
- 通过
--limit-rate用来限制HTTP请求和回应的带宽,模拟慢网速的环境。
# 将带宽限制在每秒200K字节
$ curl --limit-rate 200k https://google.com
14. -o 将服务器的回应保存成文件
- 通过
-o参数将服务器的回应保存成文件,等同于wget命令。
# 将www.example.com保存成example.html文件
$ curl -o example.html https://www.example.com
15. -O 将服务器的回应保存成文件
- 通过
-O参数将服务器回应保存成文件,并将URL的最后部分当作文件名。
# 将服务器回应保存成文件,文件名为bar.html
$ curl -O https://www.example.com/foo/bar.html
16. -s 不输出错误和进度信息
- 通过
-s参数将不输出错误和进度信息。
# 一旦发生错误,不会显示错误信息。不发生错误的话,会正常显示运行结果
$ curl -s https://www.example.com
# 想让curl不产生任何输出,可以使用下面的命令
$ curl -s -o /dev/null https://google.com
17. -S 只输出错误信息
- 通过
-S参数指定只输出错误信息,通常与-s一起使用。
# 没有任何输出,除非发生错误
$ curl -s -o /dev/null https://google.com
18. -u 设置认证的用户名和密码
- 通过
-u参数用来设置服务器认证的用户名和密码。
# 设置用户名为bob,密码为12345
# 然后将其转为HTTP标头 Authorization: Basic Ym9iOjEyMzQ1
$ curl -u 'bob:12345' https://google.com/login
# curl 能够识别URL里面的用户名和密码
$ curl https://bob:[email protected]/login
# 只设置了用户名,执行后curl会提示用户输入密码
$ curl -u 'bob' https://google.com/login
19. -v 打印调试信息
- 通过
-v参数输出通信的整个过程,用于调试。
# 打印调试信息
$ curl -v https://www.example.com
# --trace参数也可以用于调试,还会输出原始的二进制数据。
$ curl --trace - https://www.example.com
20. -x 设置请求代理
- 通过
-x参数指定HTTP请求的代理。
# 指定HTTP请求通过myproxy.com:8080的socks5代理发出
$ curl -x socks5://james:[email protected]:8080 https://www.example.com
# 如果没有指定代理协议,默认为 HTTP
$ curl -x james:[email protected]:8080 https://www.example.com
21. -X 指定请求的方法
- 通过
-X参数指定HTTP请求的方法。
# 对https://www.example.com发出POST请求
$ curl -X POST https://www.example.com