本文主要是阅读《MySQL 技术内幕》/《MariaDB 简单入门》总结而来,有需求的话可以阅读原著。

1. 查询数据
查询数据是指从数据库中获取所需要的数据,在 MariaDB 中是使用 select 语句来查询数据的。
查询的基本语法
select 属性列表 from 表名和视图列表
[where 条件表达式1]
[group by 属性名1 [having 条件表达式2]]
[order by 属性名2 [asc|desc]]
单表查询数据
- 查询所有字段:列出表的所有字段;使用
*通配符查询 - 查询指定字段:列出需要查询的字段即可
- 查询指定记录:where
- 带 in 关键字的查询:判断某个字段的值是否在指定的集合中
- 带 between and 的范围查询:匹配某个字段的值是否在指定范围内
- 带 like 的字符串匹配查询:匹配指定的字段的值
- 查询空值:判断字段的值是否为空值
- 带 and 的多条件查询:联合多个条件进行查询
- 带 or 的多条件查询:联合多个条件进行查询
- 查询结果不重复:使用 distinct 关键字去除,没有唯一约束的字段上可能存在重复的值
- 对查询结果排序:使用 order by 关键字,对某个字段进行排序
- 分组排序:使用 group by 关键字
- 用 limit 限制查询结果数量:只取出查询结果的一部分数据信息
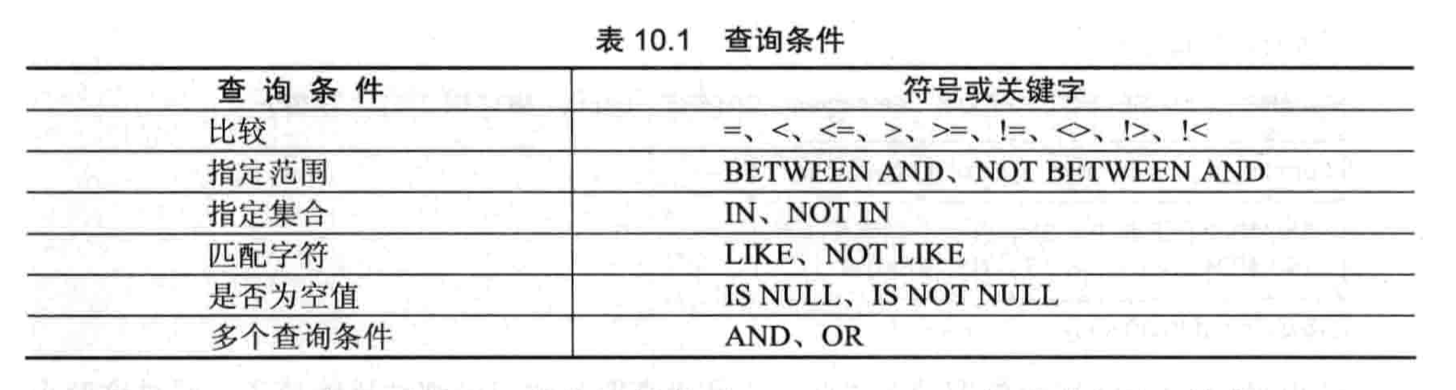
集合查询函数
- count():记录条数
- sum():记录总数
- avg():记录平均值
- max():记录最大值
- min():记录最小值
连接查询
- 内连接查询
- 外连接查询:左外连接查询、右外连接查询
- 复合条件连接查询
子查询
- 带 in 关键字的子查询
- 带比较运算符的子查询
- 带 exists 关键字的子查询
- 带 any 关键字的子查询
- 带 all 关键字的子查询
合并查询结果
- 作用场景:是将多个 select 语句的查询结果合并到一起,方便数据的查看
- union:将所有的查询结果合并到一起之后去除相同的记录
- union all:只是简单的将表合并到一起而已
- 语法格式:
select 语句1 union|union all select 语句2 union|union all ... select 语句n
为表和字段取别名
- 为表取别名:
表名 别名 - 为字段取别名:
属性名 [as] 别名
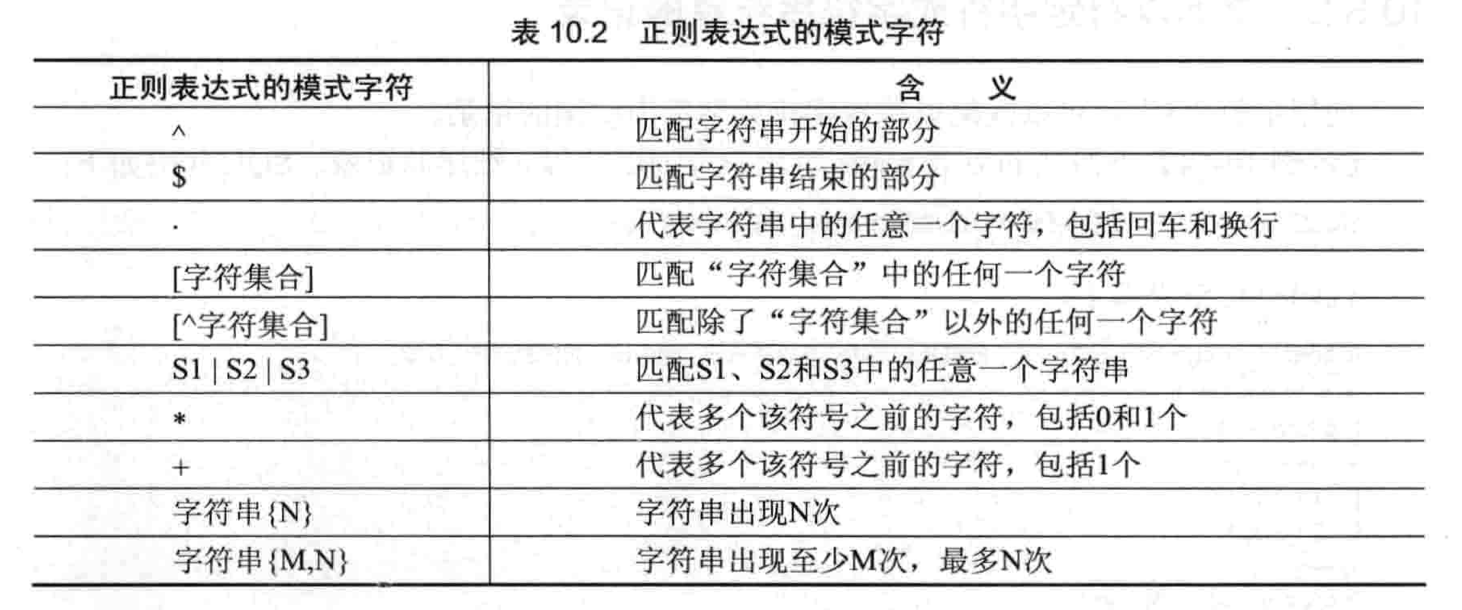
使用正则表达式
- 作用场景:用某种模式去匹配一类字符串的一个方式
- 语法格式:
属性名 regexp '匹配方式'
光说不练假把式
- 【练习 1】基本语法练习
-- 【查询的基本语法】
-- where用于指定查询条件,不指定表示查询所有记录
-- group by用于指定字段进行分组,having用于指定查询条件
-- order by用于指定字段进行排序,asc升序且默认,desc降序
sql> select num,name,age,sex from employee;
sql> select d_id,name,age,sex from employee
-> where age<26 order by d_id desc;
-- 【单表查询数据】
-- 1.查询所有字段
sql> select * from employee;
sql> select d_id,name,age,sex from employee;
-- 2.查询指定记录
sql> select * from employee where d_id=1001;
-- 3.带in关键字的查询
-- 语法格式:[not] in (元素1, 元素2, ...)
sql> select * from employee where d_id in (1001,1004);
sql> select * from employee where name not in ('张三','李四');
-- 4.带between and的范围查询
-- 语法格式:[not] between 取值1 and 取值2
sql> select * from employee where age between 15 and 25;
sql> select * from employee where not age between 15 and 25;
-- 5.带like的字符串匹配查询
-- 通配符%表示匹配多值,通配符_表示匹配单值
-- 语法格式:[not] like '字符串'
sql> select * from employee where name like 'Escape';
-- 6.查询空值
-- 语法格式:is [not] null
sql> select * from work where info is null;
-- 7.带and的多条件查询
-- 语法格式:条件表达式1 and 条件表达式2 [...]
sql> select * from employee where d_id=1001 and sex like '男';
-- 8.带or的多条件查询
-- 语法格式:条件表达式1 or 条件表达式2 [...]
sql> select * from employee where d_id=1001 or sex like '男';
sql> select * from employee where num in (1,2,3) or homeaddr like '%北京市%';
sql> select * from employee where num in (1,2,4) and age=25 or sex='女';
-- 9.查询结果不重复排序
-- 语法格式:select distinct 属性名
sql> select distinct d_id from employee;
-- 10.对查询结果排序
-- 语法格式:order by 属性名 [ass|desc]
sql> select * from employee order by age desc;
sql> select * from employee order by d_id asc, age desc;
-- 11.分组排序
-- with rollup关键字将会在所有记录的最后加上一条记录,记录所有记录的总和
-- 如果只是单独的使用分组查询,显示结果中只会显示出该分组的第一条记录信息
-- 可以和group_councat()函数一起使用,表示把每个分组中指定的字段值显示出来
-- 通常与几何函数一起使用,如count()、sun()、avg()、max()、min()等
-- 语法格式:group by 属性名 [having 条件表达式] [with rollup]
sql> select * from employee group by sex;
sql> select sex,group_concat() from employee group by sex;
sql> select sex,count() from employee group by sex;
sql> select sex,count() from employee group by sex having count(sex)>=3;
sql> select * from employee group by d_id,sex;
sql> select sex,count(sex) from employee group by sex with rollup;
-- 12.用limit限制查询结果数量
-- 语法格式:limit 初始位置,记录数
sql> select * from employee limit 2;
sql> select * from employee limit 0,2;
-- 【集合查询函数】
-- 1.count()函数
sql> select d_id,count(*) from employee group by d_id;
-- 2.sum()函数
sql> select num,sum(score) from grade where num=1001;
-- 3.avg()函数
sql> select avg(age) from employee;
sql> select course,avg(score) from grade group by course;
-- 4.max()函数
sql> select max(age) from employee;
sql> select num,course,max(score) from grade group by course;
-- 5.min()函数
sql> select min(age) from employee;
sql> select course,min(score) from grade group by course;
-- 【连接查询】
-- 1.内连接查询
sql> select num,name,employee.d_id,age,sex,d_name,function
-> from employee,department
-> where emplyee.d_id=department.d_id;
-- 外连接查询
-- 语法格式:select 属性名列表 from 表名1 left|right join 表名2 on 表名1.属性名1=表名2.属性名2;
-- 2.左外连接查询
-- 可以查询表1中的所有记录,而表2中只能查询出匹配的记录
sql> select num,name,employee.d_id,age,sex,d_name,function
-> from employee left join department
-> on emplyee.d_id=department.d_id;
-- 3.右外连接查询
-- 可以查询表2中的所有记录,而表1中只能查询出匹配的记录
sql> select num,name,employee.d_id,age,sex,d_name,function
-> from employee right join department
-> on emplyee.d_id=department.d_id;
-- 4.复合条件连接查询
sql> select num,name,employee.d_id,age,sex,d_name,funcion
-> from employee,department
-> where employee.d_id=department.d_id and age>24;
sql> select num,name,employee.d_id,age,sex,d_name,funcion
-> from employee,department
-> where employee.d_id=department.d_id order by age desc;
-- 【子查询】
-- 1.带in关键字的子查询
sql> select * from employee where d_id in (select d_id from department);
sql> select * from employee where d_id not in (select d_id from department);
-- 2.带比较运算符的子查询
-- 从scholarship表中查询出一等奖学金要求的最低分,然后从computer_stu中筛选
sql> select id,name,score from computer_stu
-> where score>=(select score from scholarship where level=1)
sql> select d_id,d_name from department
-> where d_id!=(select d_id from employee where age=24);
-- 3.带exists关键字的子查询
-- 子查询将返回真或假值,如果为真则执行外层查询
sql> select * from employee where exists (select d_name from department where d_id=1003);
sql> select * from employee where not exists (select d_name from department where d_id=1003);
sql> select * from employee where age>24 and
-> exists (select d_name from department where d_id=1003);
-- 4.带any关键字的子查询
-- any表示满足其中任一条件,即可执行外层查询
sql> select * from computer_stu where score>=any(select score from scholarship);
-- 5.带all关键字的子查询
-- all表示必须满足所有条件,才可以执行外层查询语句
sql> select * from computer_stu where score>=all(select score from scholarship);
-- 【合并查询结果】
-- 1.union
sql> select d_id from department union select d_id from department;
-- 2.union all
sql> select d_id from department union all select d_id from department;
-- 【为表和字段取别名】
-- 1.为表取别名
sql> select * from department dep where dep.d_id=1001;
-- 2.为字段取别名
sql> select d_id as department_id, d_name as department_name from department;
-- 3.综合
sql> select d_id as dep_id, d_name as dep_name from department dep where dep.d_id=1001;
-- 【使用正则表达式查询】
-- 1.查询以特定字符或字符串开头的记录
sql> select * from info where name regexp '^E';
-- 2.查询以特定字符或字符串结尾的记录
sql> select * from info where name regexp 'e$';
-- 3.用字符点来替代字符串中的任意一个字符
sql> select * from info where name regexp '^Esc..e$';
-- 4.匹配指定字符中的任意一个
sql> select * from info where name regexp '[ceo]';
-- 5.匹配指定字符以外的字符
sql> select * from info where name regexp '[^a-w0-9]';
-- 6.匹配指定字符串
sql> select * from info where name regexp 'ic';
-- 7.使用*和+来匹配多个字符
sql> select * from info where name regexp 'a*c';
sql> select * from info where name regexp 'a+c';
-- 8.使用{M}或者{M,N}来指定字符串连续多线的次数
sql> select * from info where name regexp 'a{3}';
sql> select * from info where name regexp 'a{1,3}';
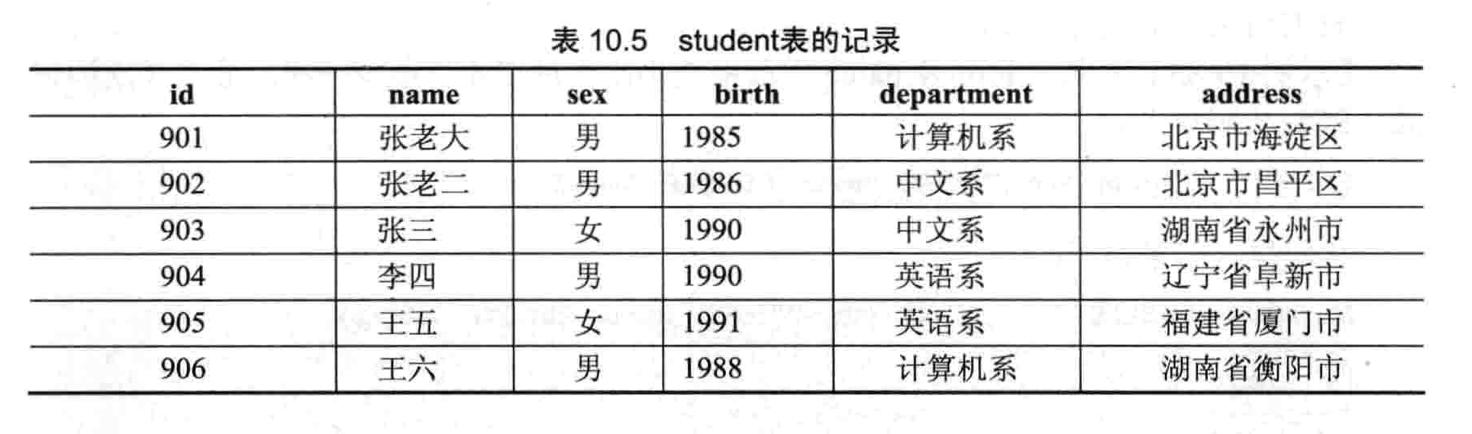
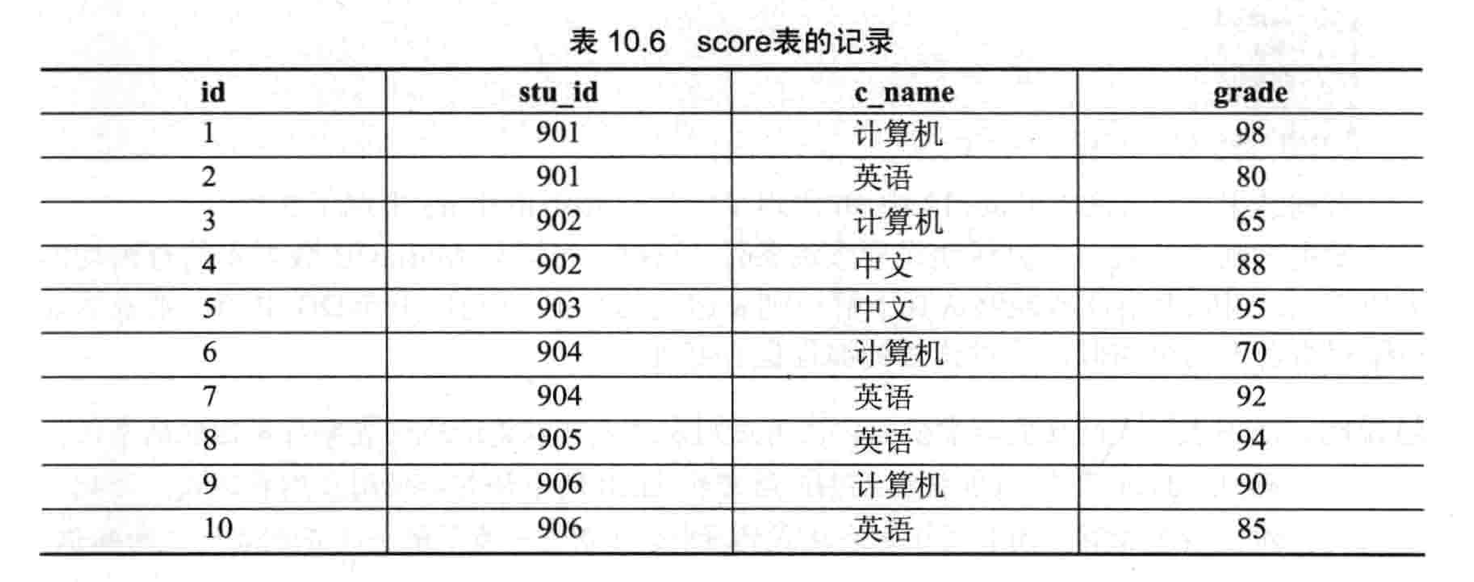
- 【练习 2】将在 student 和 score 表上进行查询
- 创建 student 和 score 表并插入数据
- 查询 student 表的所有记录
- 查询 student 表中的第 2 到 4 条记录
- 从 student 表查询所有学生的序号、姓名和院系信息
- 从 student 表中查询计算机系和英语系的学生信息
- 从 student 表中查询年龄为 18-22 岁的学生信息
- 从 student 表中查询每个院系有多少人
- 从 score 表中查询每个科目的最高分
- 查询李四的考试科目和考试成绩
- 用连接查询的方式查询所有学生的信息和考试信息
- 计算每个学生的总成绩
- 计算每个考试科目的平均成绩
- 查询计算机成绩低于 95 的学生的信息
- 查询同时参见计算机和英语考试的学生的信息
- 将计算机考试成绩按照从高到低进行排序
- 从 student 和 score 表中查询出学生的学号,然后合并查询结果
- 查询姓张或者姓王的同学的姓名、院系和考试科目以及成绩
- 查询都是湖南的学生的姓名、年龄、院系和考试科目以及成绩
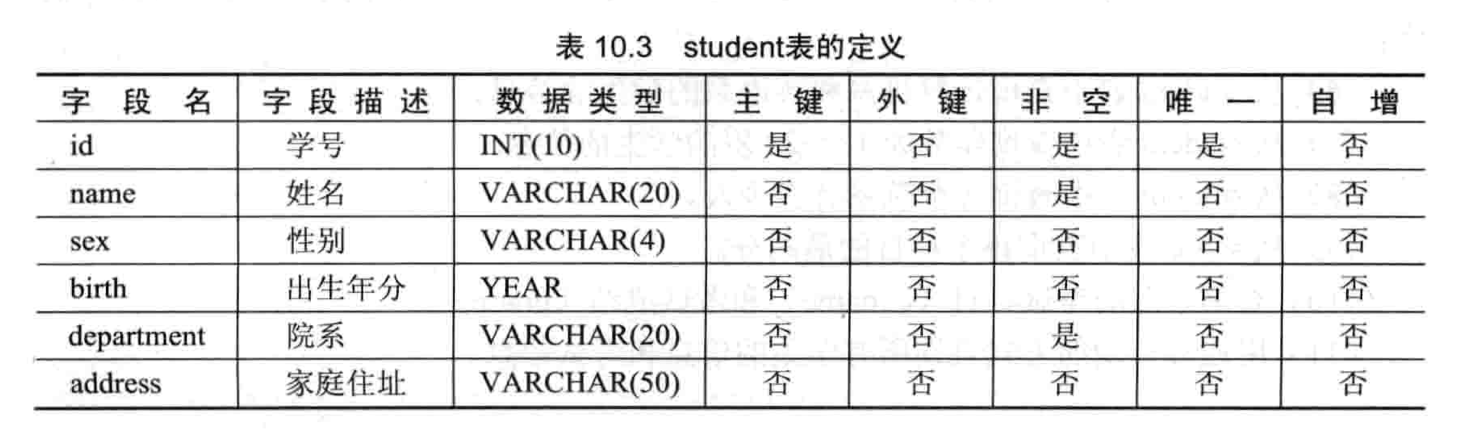
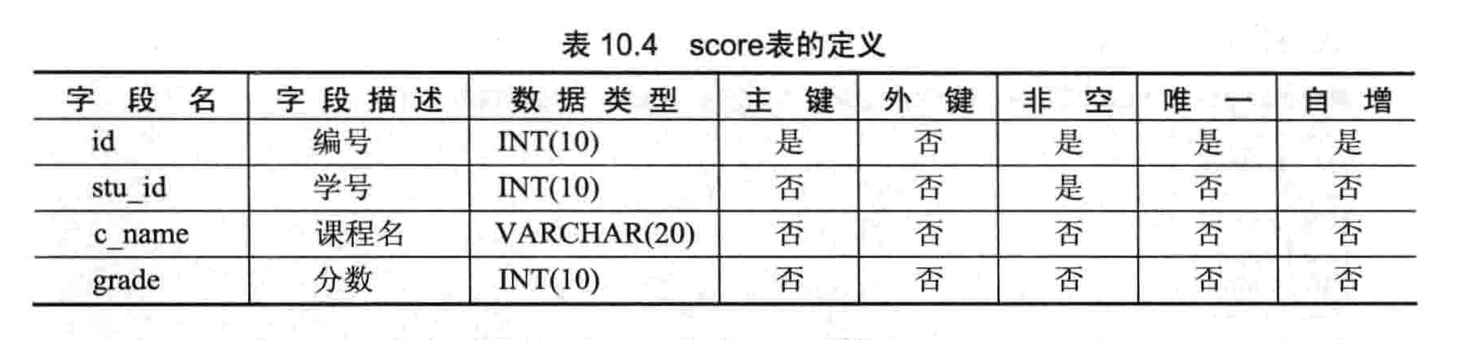
-- 1.创建student和score表并插入数据
sql> create table student(
-> id int(10) not null unique primary key,
-> name varchar(20) not null,
-> sex varchar(4),
-> birth year,
-> department varchar(20),
-> address varchar(50)
-> );
sql> create table score(
-> id int(10) not null unique primary key auto_increment,
-> stu_id int(10) not null,
-> c_name varchar(20),
-> grade int(10)
-> );
-- 2.查询student表的所有记录
sql> select * from student;
sql> select id,name,sex,birth,department,address from student;
-- 3.查询student表中的第2到4条记录
sql> select * from student limit 1,3;
-- 4.从student表查询所有学生的序号、姓名和院系信息
sql> select id,name,department from student;
-- 5.从student表中查询计算机系和英语系的学生信息
sql> select * from student where department in ('计算机系','英语系');
sql> select * from student where department='计算机系' or department='英语系';
-- 6.从student表中查询年龄为18-22岁的学生信息
sql> select * from student where age between 18 and 22;
sql> select * from student where age>=18 and age<=22;
-- 7.从student表中查询每个院系有多少人
sql> select department, count(id) as sum_of_dep from student group by department;
-- 8.从score表中查询每个科目的最高分
sql> select c_name,max(grade) from score group by c_name;
-- 9.查询李四的考试科目和考试成绩
sql> select c_name,grade from score where stu_id=(select id from student where name='李四');
-- 10.用连接查询的方式查询所有学生的信息和考试信息
sql> select student.id,name,sex,birth,department,address,c_name,grade
-> where student,score where student.id=score.stu_id;
sql> select s1.id,name,sex,birth,department,address,c_name,grade
-> where student s1, socre s2 where s1.id=s2.stu_id;
-- 11.计算每个学生的总成绩
sql> select std_id,sum(grade) from score group by stu_id;
sql> select student.id,name,sum(grade) from student,score
-> where student.id=score.stu_id group by student.id;
-- 12.计算每个考试科目的平均成绩
sql> select c_name,avg(grade) from score group by c_name;
-- 13.查询计算机成绩低于95的学生的信息
sql> select * from student where id in
-> (select stu_id from score where c_name="计算机" and grade<95);
-- 14.查询同时参见计算机和英语考试的学生的信息
sql> select * from student where id=any(
-> select stu_id from score where stu_id in
-> (select stu_id from score where c_name='计算机') and c_name='英语'
-> );
-- 15.将计算机考试成绩按照从高到低进行排序
sql> select stu_id,grade from score where c_name='计算机' order by grade desc;
-- 16.从student和score表中查询出学生的学号,然后合并查询结果
sql> select id from student union select stu_id from score;
-- 17.查询姓张或者姓王的同学的姓名、院系和考试科目以及成绩
sql> select student.id,name,department,grade from studen,score
-> where student.id=score.stu_id and (name like '张%' or name like '王%');
-- 18.查询都是湖南的学生的姓名、年龄、院系和考试科目以及成绩
sql> select student.id,name,department,grade from studen,score
-> where student.id=score.stu_id and address like '湖南%';
常见问题以及解答
- 【问题 1】通配符和正则表达式的区别?
- 虽然两则都可以进行字符串匹配,但是通配符需要结合 like 关键字一起使用且适用范围有限,只能由于有限的模糊查询上。而正则表达式需要和 regexp 关键字一起使用且非常灵活,可以用于复杂的匹配上。
- 【问题 2】集合函数必须要用 group by 关键字吗?
- 集合函数可以不与 group by 关键字一起使用,但是集合函数一般情况还是一起使用的。主要是因为集合函数通常都是用来计算某一类数据的总量、平均值等,所有经常使用 group by 来进行分组,然后再进行集合运算。
2. 增删改查数据
数据库通过插入、更新和删除等方式来改变表中的记录。
插入数据
- 为标的所有字段插入数据:
insert into 表名 values(值1, 值2, ..., 值n); - 为表中的指定字段插入数据:
insert into 表名(属性1, ..., 属性n,) values(值1, ..., 值n); - 同时插入多条数据记录:
inset into 表名 [(属性列表)] values(取值列表1), ..., (取值列表n); - 将查询结果插入到表中:
insert into 表名1(属性列表1) select 属性列表2 from 表名2 where 条件表达式;
更新数据
- 语法格式
update 表名 set 属性名1=取值1, ..., 属性名n=取值n where 条件表达式;
删除数据
- 语法格式
delete from 表名 [where 条件表达式];
光说不练假把式
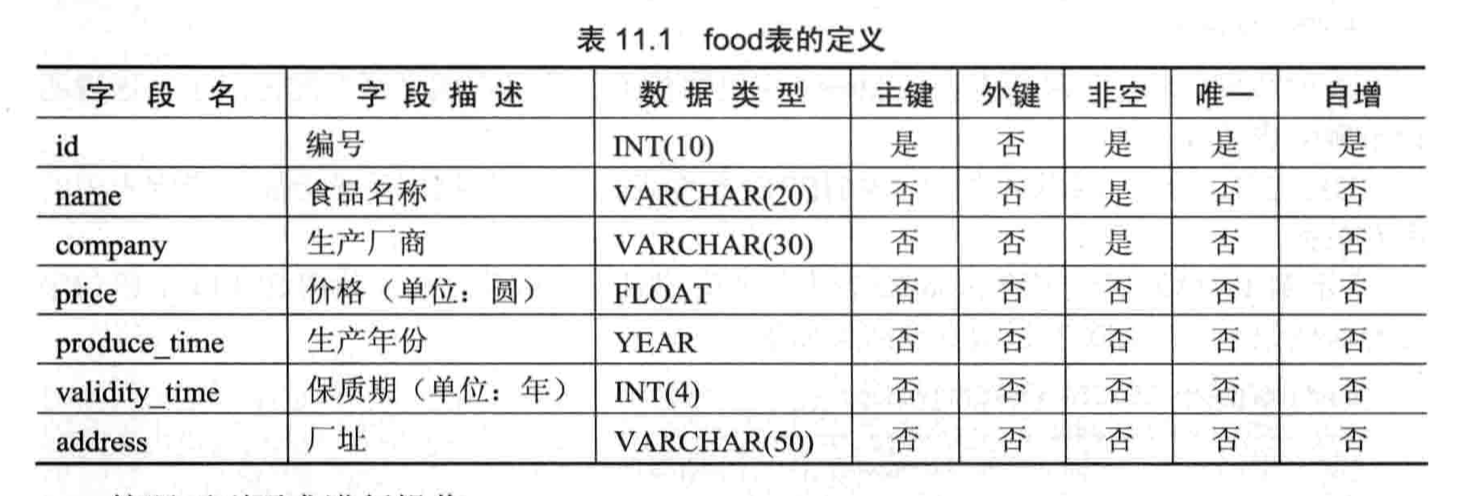
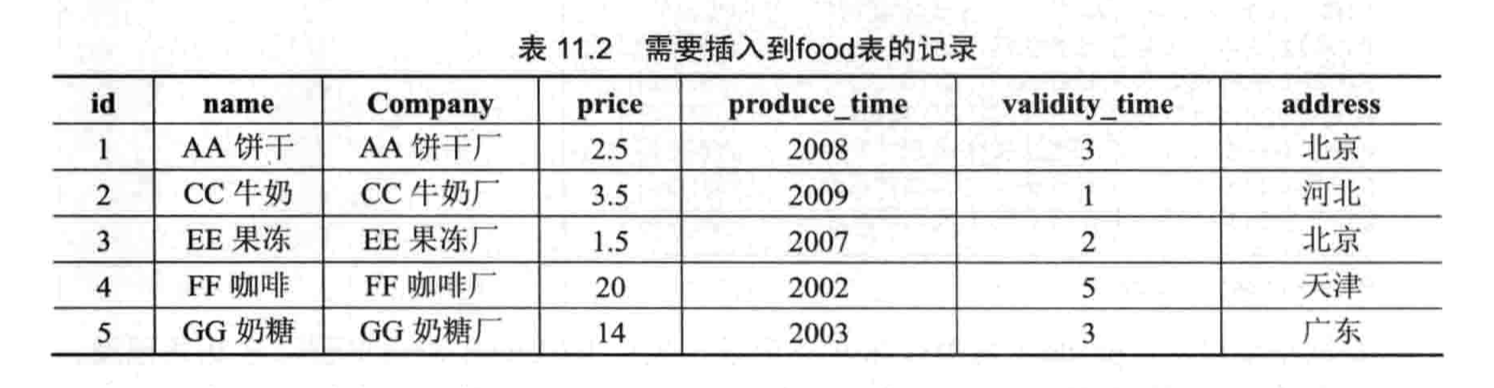
- 【练习】将在 food 表上进行增删改查数据
- 建表并插入数据
- 将《CC 牛奶厂》的地址改为《内蒙古》,并且将价格改为 3.2
- 将厂址在北京的公司的保质期都改为 5 年
- 删除过期食品的记录
- 删除厂址为北京的产品的记录
-- 1.建表
sql> create table food(
-> id int(10) not null unique primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20) not null,
-> company varchar(30) not null,
-> price float,
-> produce_time year,
-> validity_time int(4),
-> address varchar(50)
-> );
-- 2.插入数据
-- 多种插入方式,单插、多插
sql> insert into food values(1, 'AA饼干', 'AA饼干厂', 2.5, '2018', 3, '北京');
sql> insert into food(id,name,company,price,produce_time,validity_time,address)
-> values(2, 'CC牛奶', 'CC牛奶厂', 3.5, '2016', 1, '河北');
sql> insert into food values
-> (null, 'EE果冻', 'EE果冻厂', 1.5, '2017', 2, '北京'),
-> (null, 'FF咖啡', 'FF咖啡厂', 20, '2012', 5, '天津'),
-> (null, 'GG奶糖', 'GG奶糖厂', 14, '2013', 3, '广东');
-- 3.将《CC牛奶厂》的地址改为《内蒙古》,并且将价格改为3.2
sql> update food set address='内蒙古', price=3.2 where name='CC牛奶厂';
-- 4.将厂址在北京的公司的保质期都改为5年
sql> update food set validity_time=5 where address='北京';
-- 5.删除过期食品的记录
sql> delete from food where 2018-produce_time>validity_time;
-- 6.删除厂址为北京的产品的记录
sql> delete from food where address='北京';
常见问题以及解答
- 【问题 1】如何为自增字段赋值?
- [方法一] 在 insert 语句中不为该字段赋值
- [方法二] 在 insert 语句中将字段赋值为 null
- 【问题 2】如何进行联表删除?
- 如果某个学生退学了,就必须在学生表、成绩表、图书表等一并进行删除,这就是进行联表删除。这个可以通过外键来实现。其他表中的信息与学生表中的信息都是通过学号来联系的,可以根据学号查询存在该学生信息的表,删除相应的数据即可。
3. 运算符
运算符是用来连接表达式中各个操作数的符号,其作用是用来指明对操作数所进行的与运算。
- 算数运算符
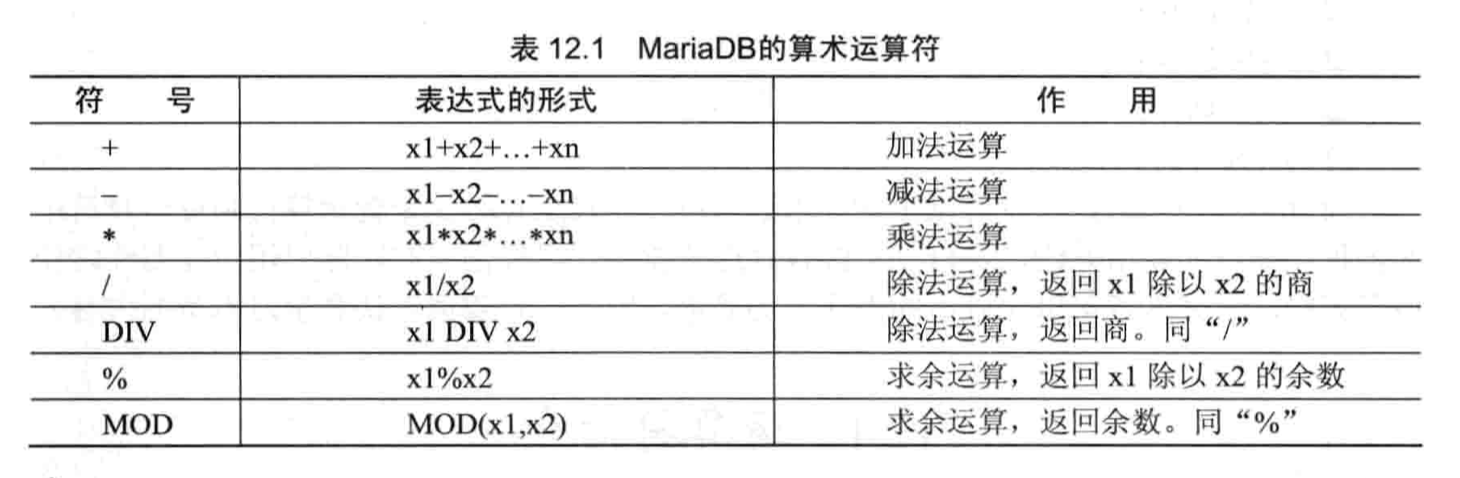
- 比较运算符
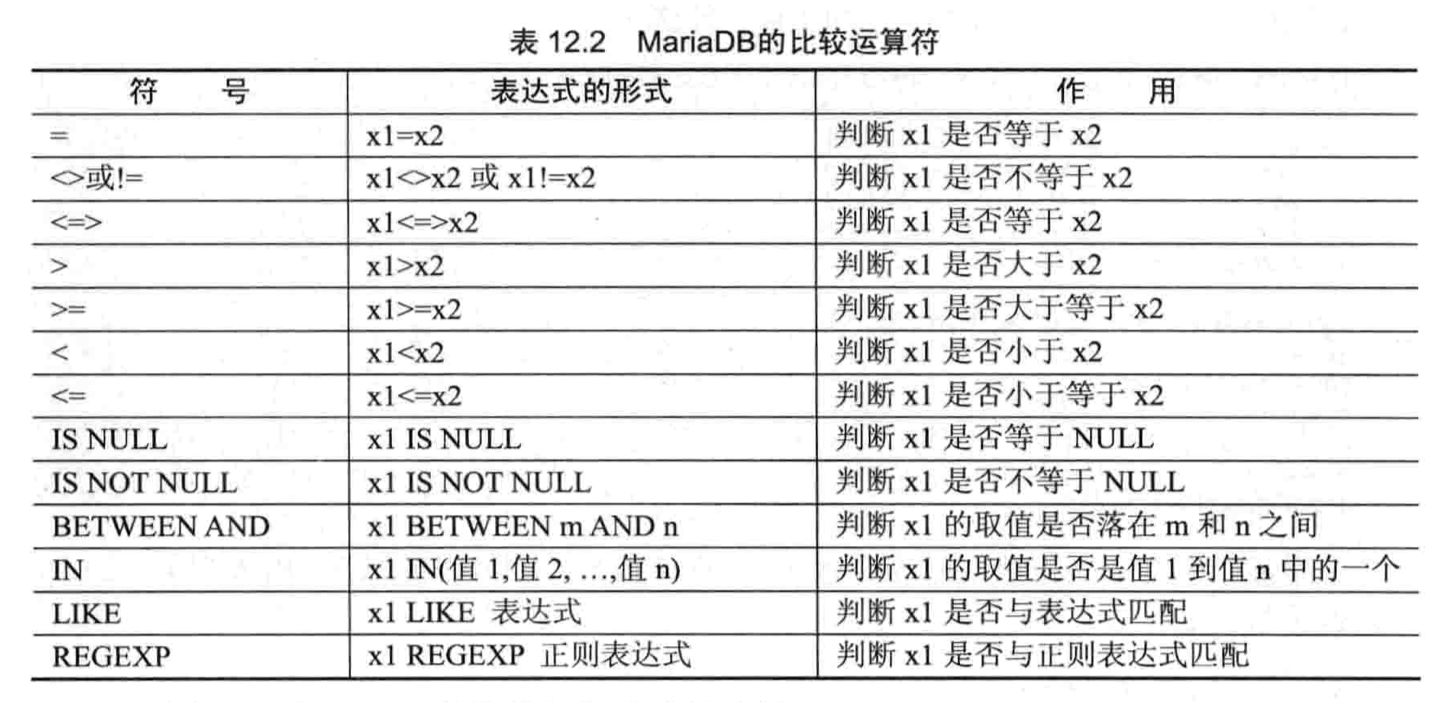
- 逻辑运算符
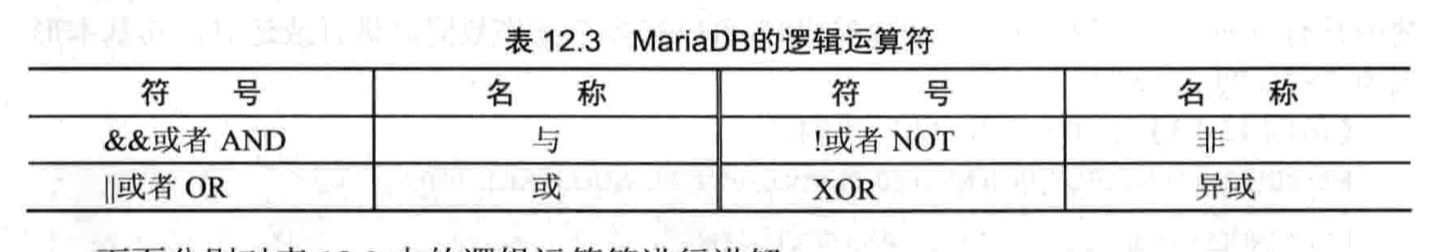
- 位运算符
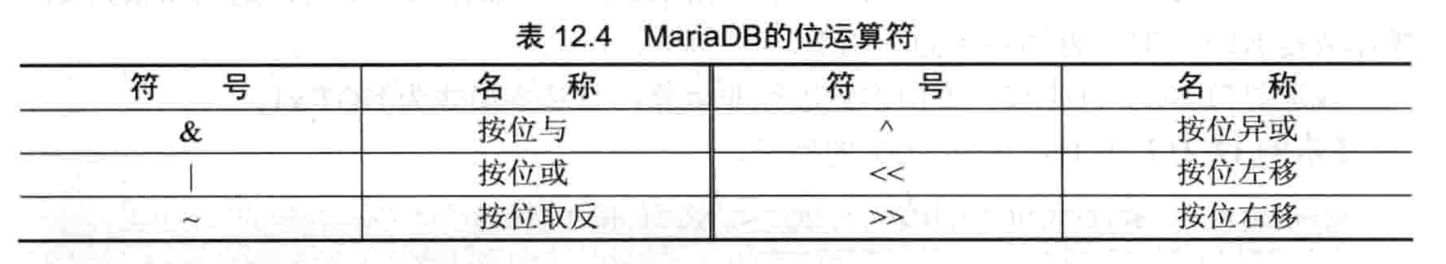
- 运算符优先级
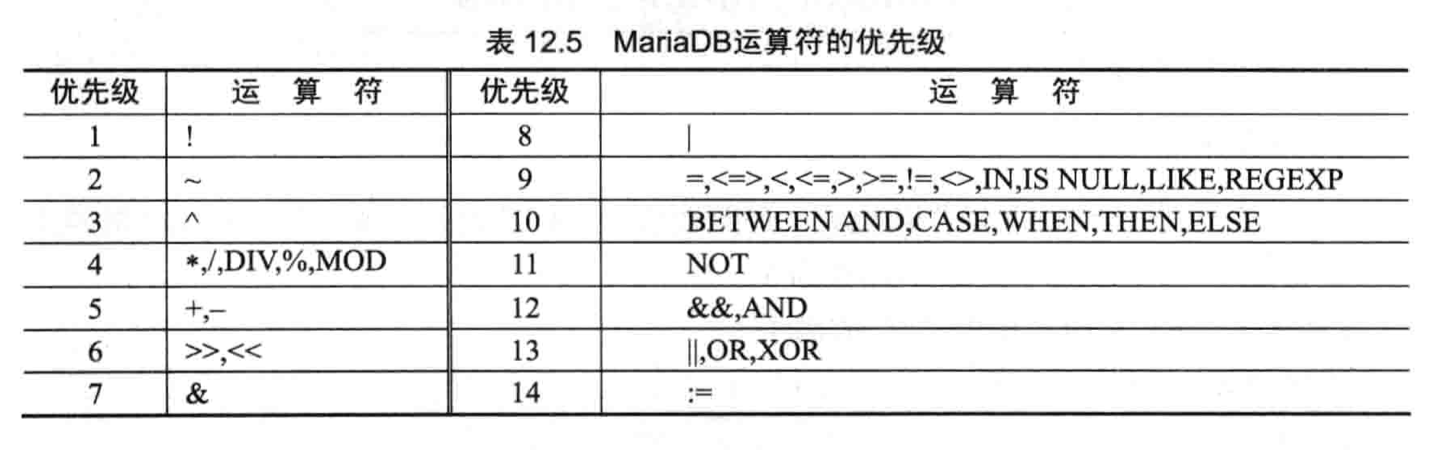
光说不练假把式
- 【练习】基础知识练习
-- 1.算数运算符
sql> select num,num+5,num-3,num*4 from department;
sql> select num,num/3,num div 3,num%3,mod(num,3) from department;
-- 2.比较运算符
sql> select num,num=24,num=20 from department;
sql> select 'b'='b','b'='c';
sql> select num,num<23,num<=25 from department;
sql> select num,num is null, num is not null from department;
sql> select num,num between 20 and 28 from department;
sql> select 'b' between 'a' and 'd';
sql> select num,num in (2,20,24,28) from department;
sql> select name,name like 'Escape' from department;
sql> select name,name regexp '^E' from department;
-- 3.位运算符
sql> select -1&&2&&3, 0&&3, 0&&null, 3&&null;
sql> select 1||-1, null||0, 3||null, 0||null, null||null, 0||0;
sql> select !1, !0.3, !-3, !0, !null;
-- 4.位运算符
sql> select 5&6, 5&6&7;
sql> select 5|6, 5|6|7;
sql> select ~1;
sql> select 5^6;
sql> select 5<<2;
sql> select 5>>2;
常见问题以及解答
- 【问题 1】比较运算符的结果只能是 0 和 1 吗?
- 在 MariaDB 中,比较运算符是来判断运算符两边的操作数的大小关系。所有,比较比较运算符的结果只有 0 和 1.不仅比较运算符只如此,逻辑运算符的结果也只有 0 和 1。
- 【问题 2】十进制的数也可以直接使用位运算符吗?
- 在进行位运算时,数据库系统会先将所有的操作数转化成二进制数,然后将这些二进制进行位运算,最后将这些运算结果转换成十进制数显示。所有,位运算符的操作数是十进制。十进制数和二进制数的互换是数据库系统实现的。因此,位运算的操作数必须是十进制数,否则计算的结果就会使错误的。在使用位运算符时,如果操作数是二进制数、八进制数、十六进制数时,要先通过 conv()函数将操作数转换成十进制数,然后才能进行相应的位运算。
4. 函数
在 MariaDB 数据库中提供了很丰富的函数,通过这些函数,可以简化用户的操作。
- 数学函数
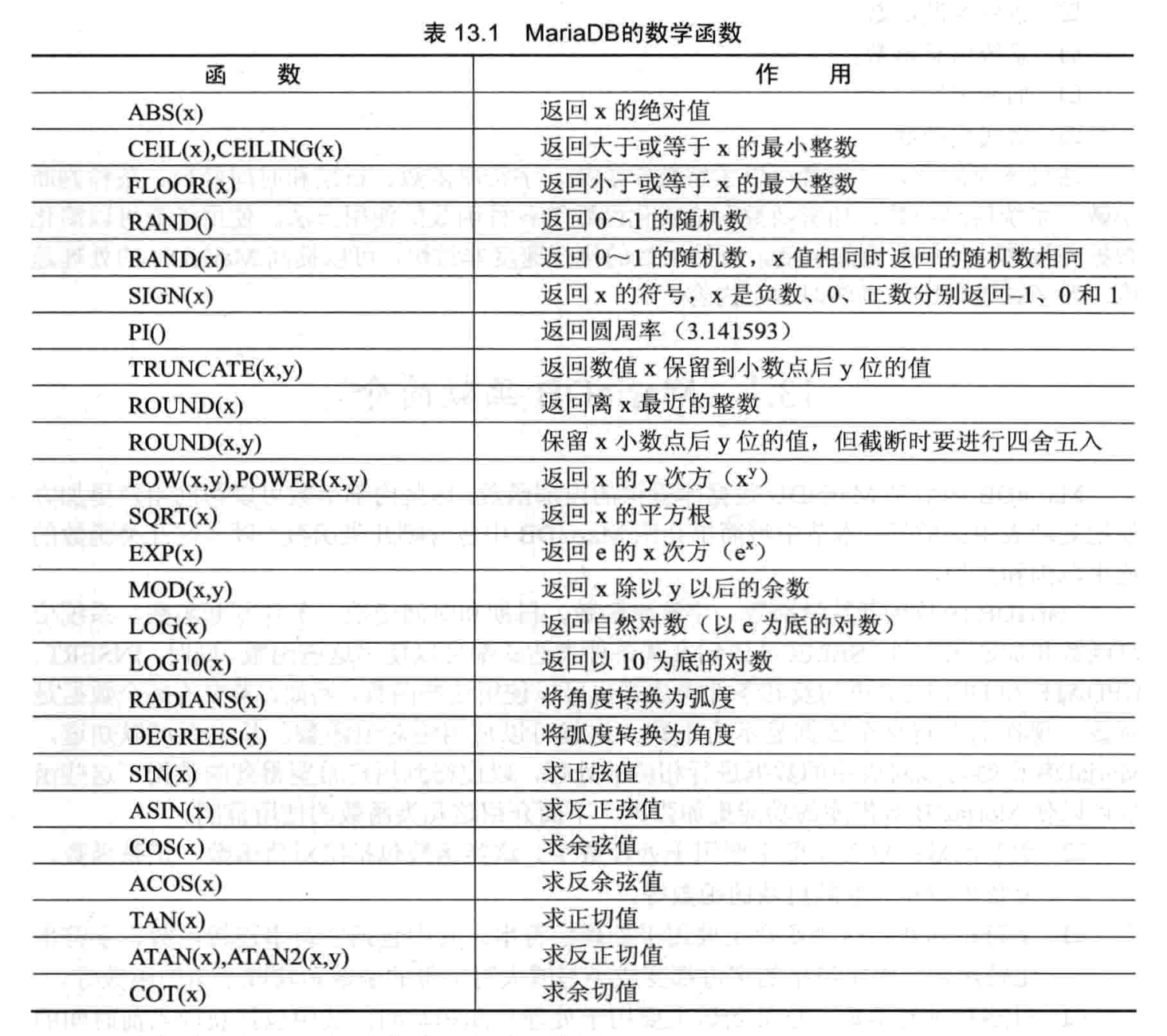
- 字符串函数

- 日期和时间函数
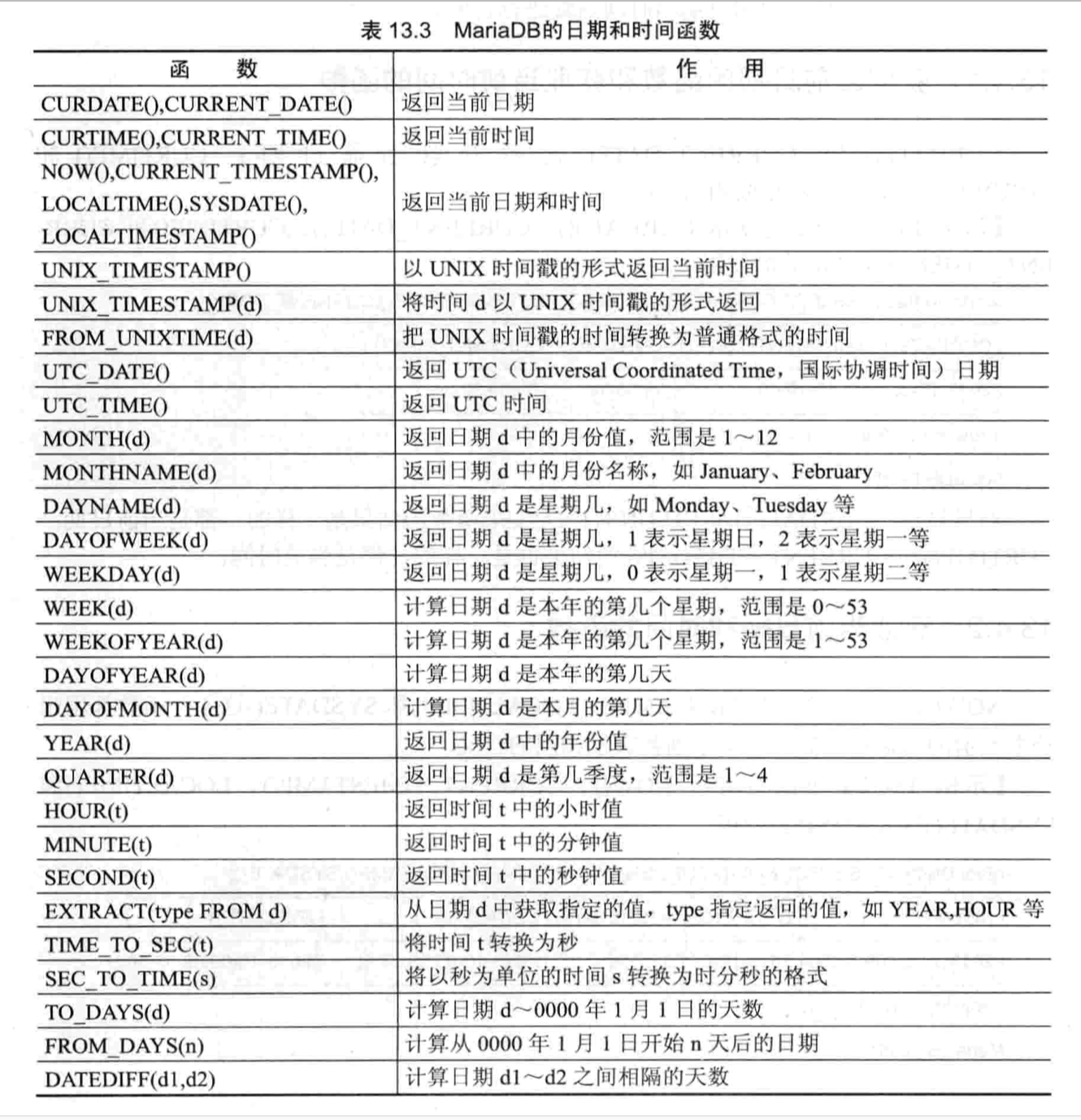
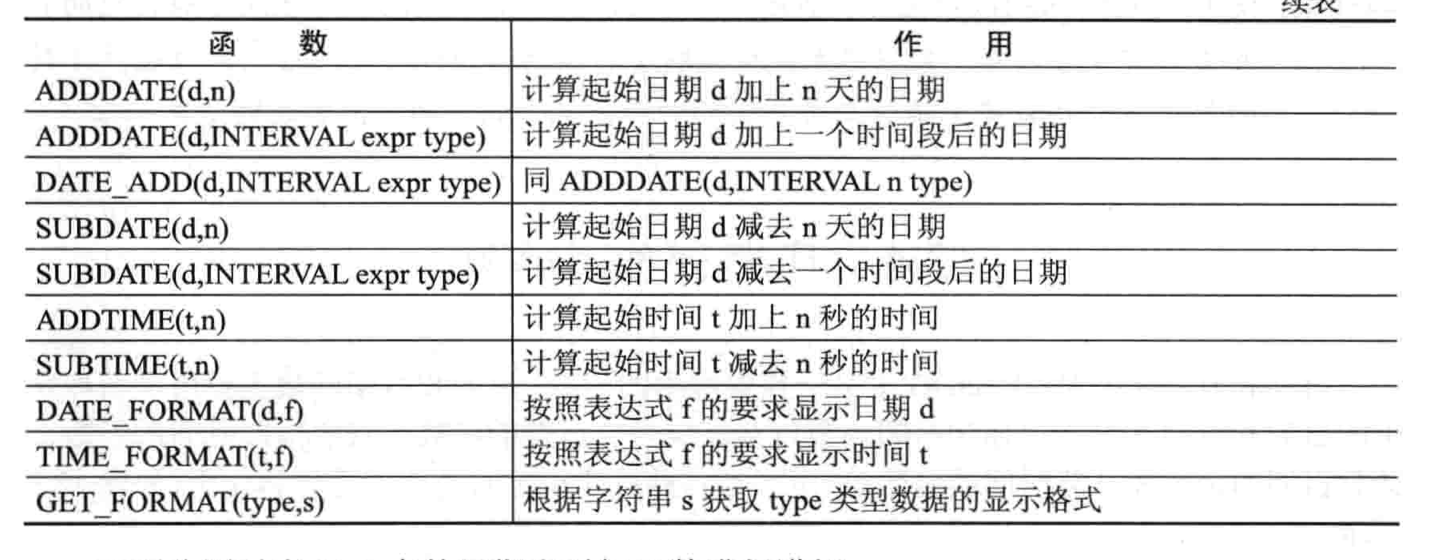
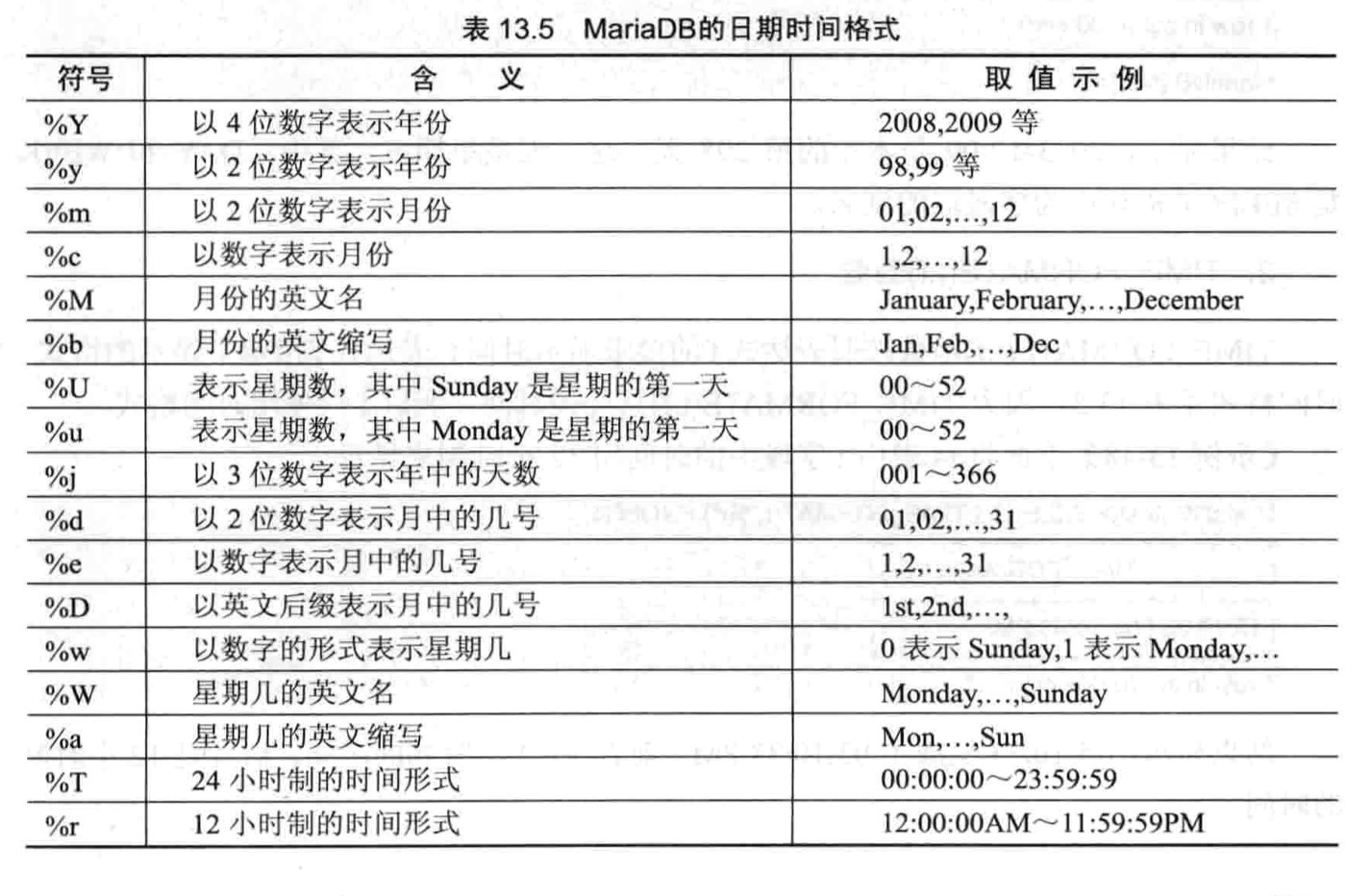
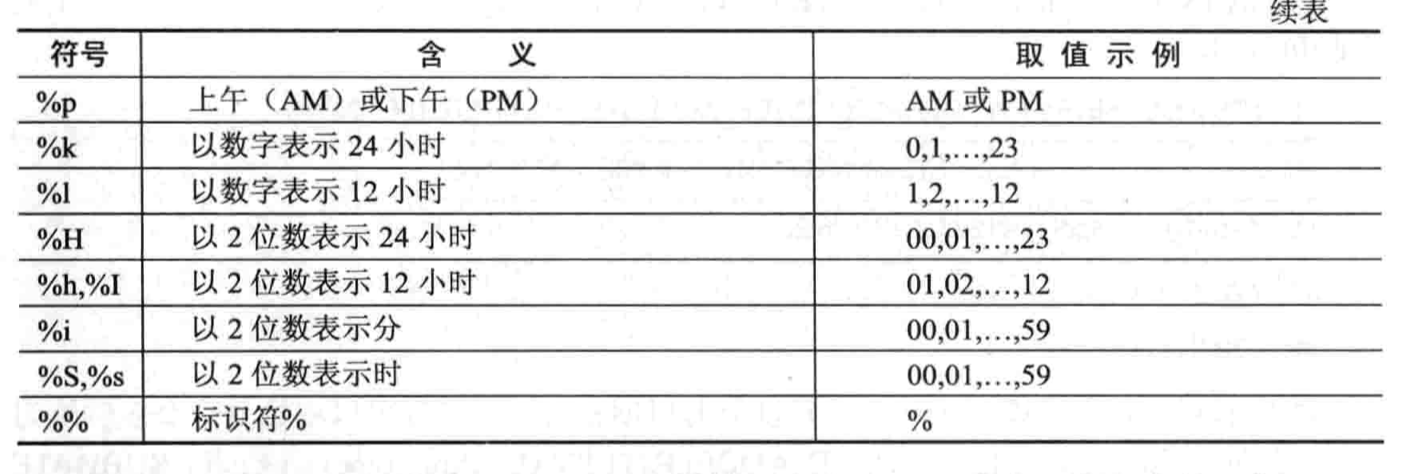
条件判断函数
if(expr, v1, v2)ifnull(v1, v2)case when expr1 then v1 [when expr2 then v2 ...] [else vn] end
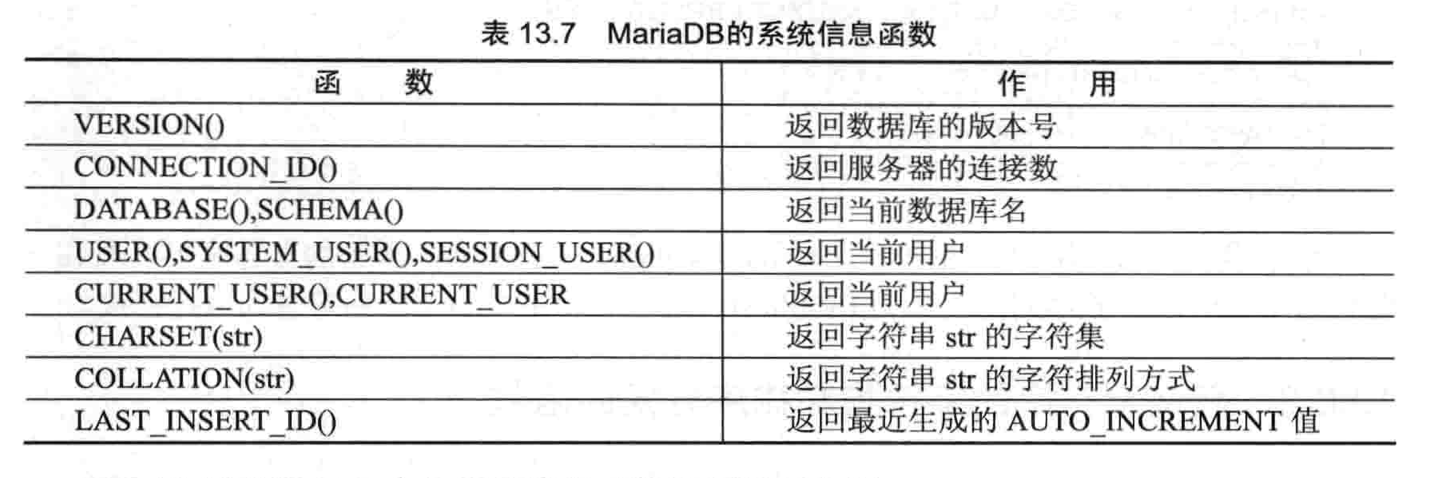
系统信息函数
加密函数
password(str)md5(str)encode(str,pswd_str)decode(crypt_str,pswd_str)
格式化函数
format(x,n):格式化取余数的函数ascii(s):返回 ASCII 码的函数bin(s):返回二进制的函数hex(s):返回十六进制的函数oct(s):返回八进制的函数conv(s1,s2):进制转换的函数inet_aton(ip)、inet_ntoa(n):IP 地址与数字相互转换的函数get_loct(name,time):加锁函数is_free_lock(name):解锁函数benchmark(num,expr):重复执行某个函数convert(s using cs):改变字符集函数cast(x as type)/convert(x,type):改变字段函数类型的函数
光说不练假把式
- 【练习】基本知识点练习
-- 1.数学函数
sql> select abs(0.5),abs(-0.5),pi(),sqrt(16);
-- 2.字符串函数
sql> select name,char_length(name),length(name) from department;
sql> select concat('bei','ji','ng'), concat_ws('-','bei','ji','ng');
-- 3.日期和时间函数
sql> select curdate(),current_date(),curtime(),current_time();
sql> select new(),current_timestamp(),localtime(),sysdate();
sql> select date,date_fromat(date,'%b %D %Y') from sys_info;
-- 4.条件判断函数
sql> select id,grade,if(grade>=60,'pass','fail') from student;
sql> select id,ifnull(grade,'no grade') from student;
sql> select id,grade
-> case
-> when grade>60 then 'good'
-> when grade=60 then 'pass'
-> else 'fail'
-> end level from student;
-- 5.系统信息函数
sql> select version();
-- 6.加密函数
sql> select password('admin');
-- 7.格式化函数
sql> selct fromat(234.333,2);
sql> select benchmark(1000, now());
sql> select charset('ABC'),charset(convert('ABC' using gbk));
sql> select dt,case(dt as date),convert(dt,time) from department;
5. 存储过程和函数
- 【练习 1】
--
sql>
--
sql>
--
sql>
- 【练习 2】
--
sql>
--
sql>
--
sql>
常见问题以及解答
- 【问题 1】



